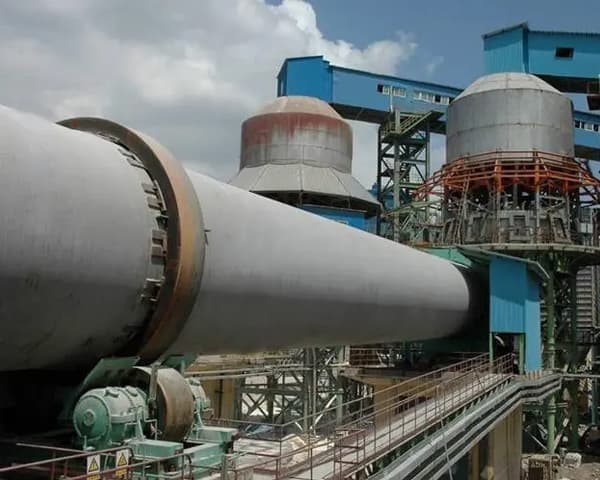
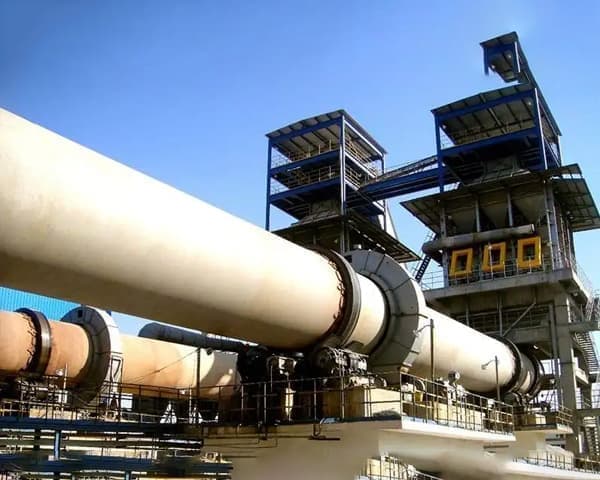
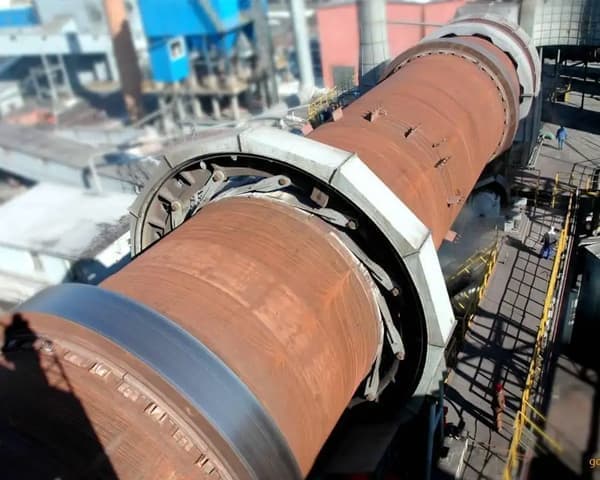
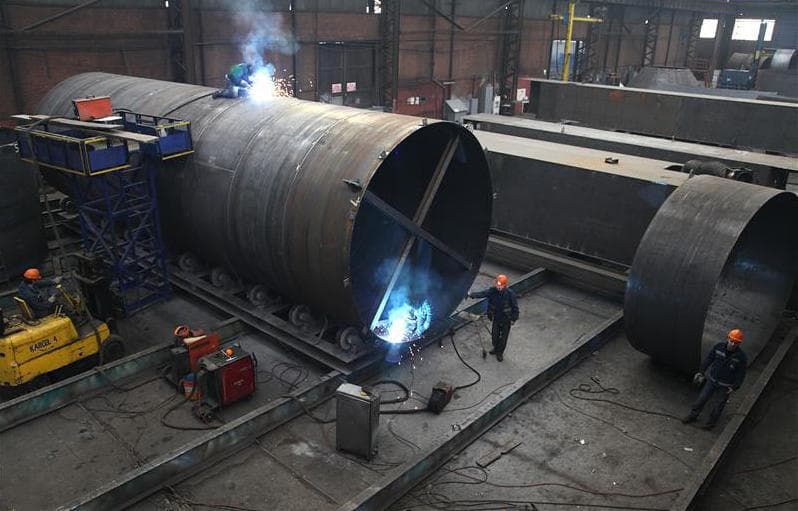
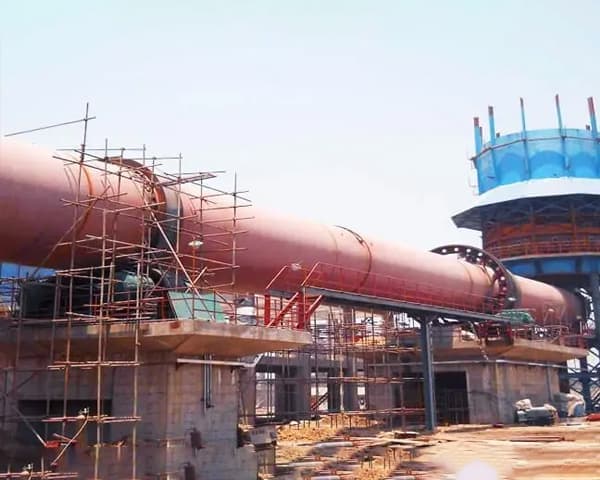
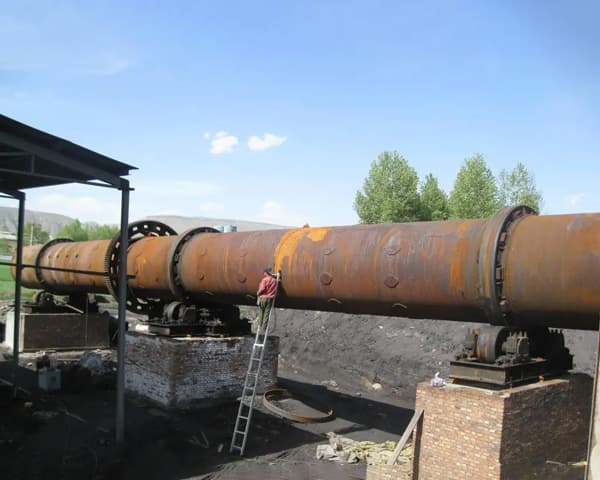
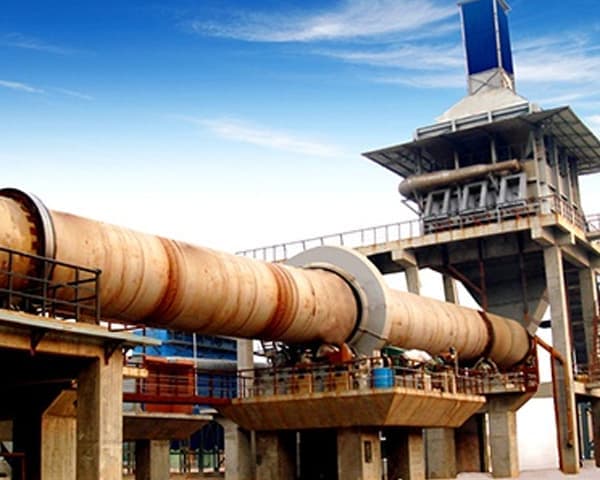
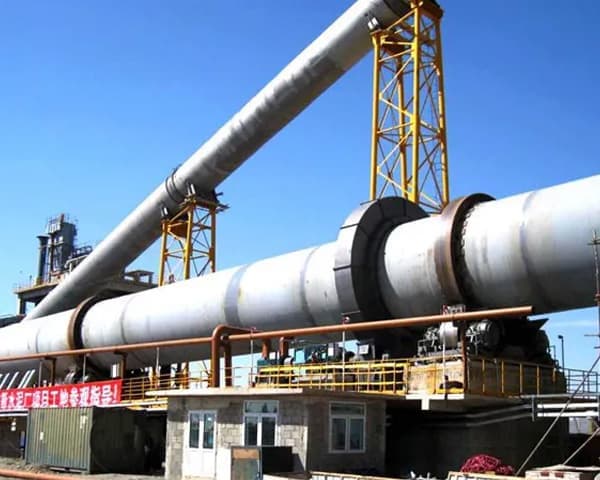
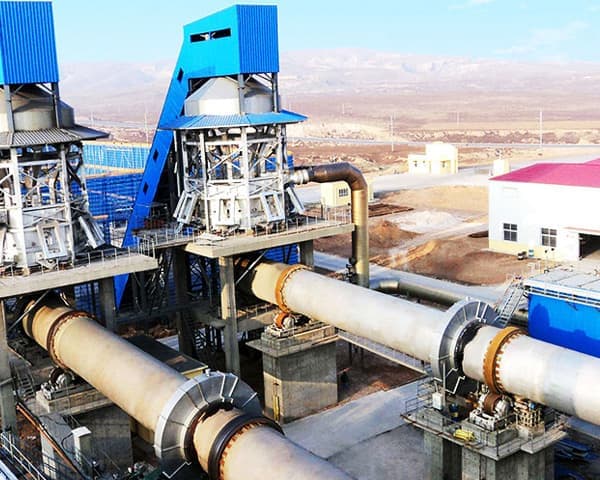
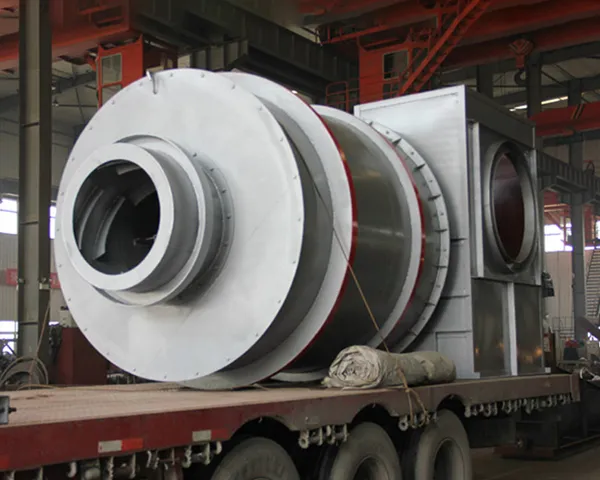
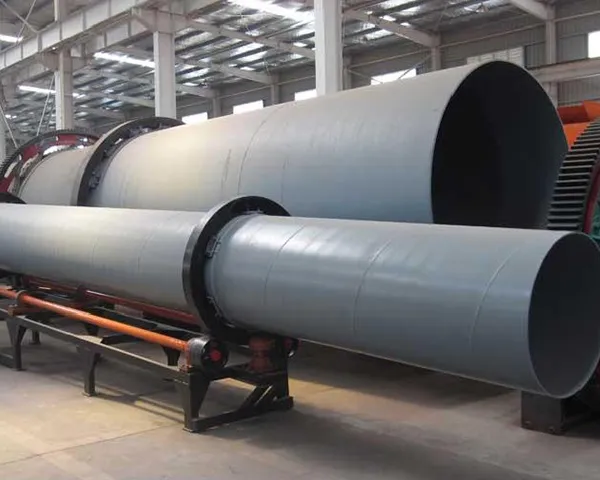
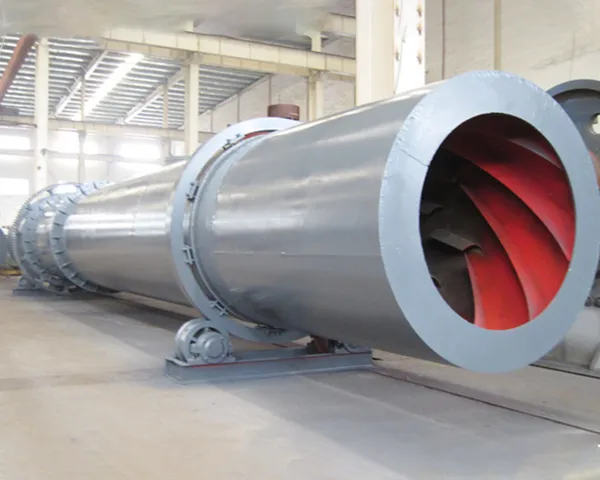
Metallurgical rotary kiln Product Description
Metallurgical rotary kiln is also called metallurgical chemical kiln or metallurgical kiln, is mainly used in the metallurgical industry, iron plant poor iron ore magnetization roasting; chrome, nickel iron ore oxidation roasting; refractory plant roasting high metallurgical ore and aluminum plant roasting clinker, aluminum hydroxide, chemical plant roasting chrome ore sand and chrome ore powder and other types of minerals.

Metallurgical rotary kiln Working Principle
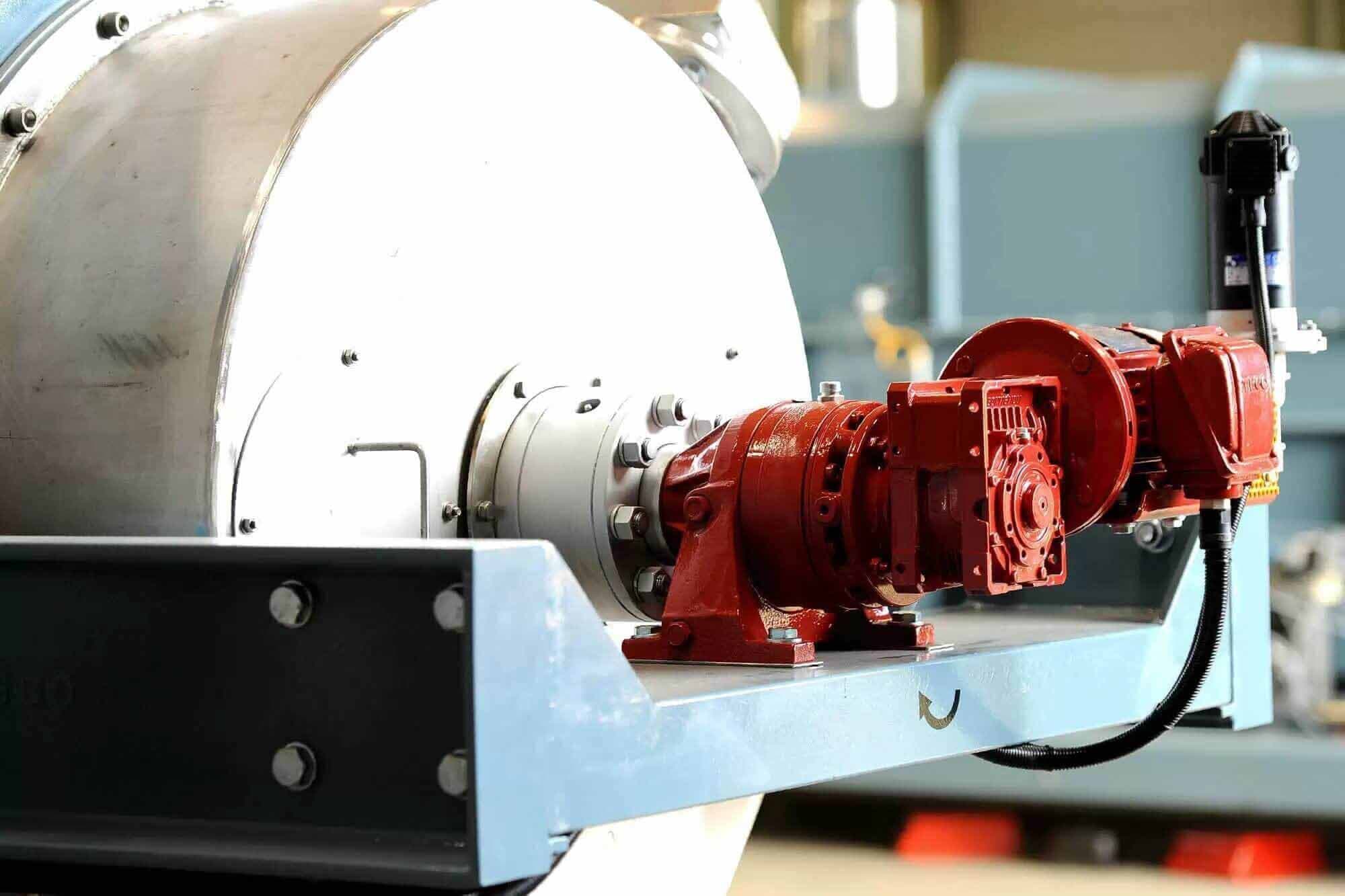
In normal operation, the metallurgical rotary kiln is driven by the main drive motor, which transmits power to the open gear unit via the main reducer.
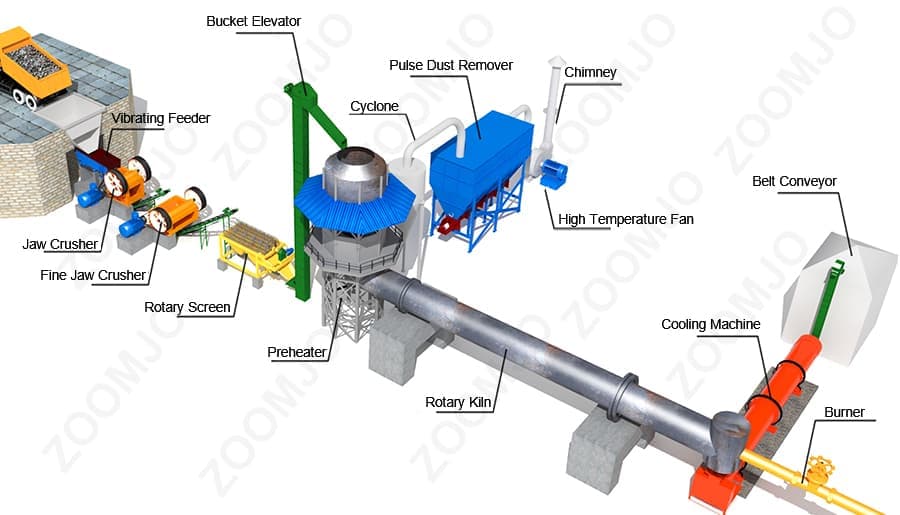
The material enters the kiln from the end of the kiln (at the top end of the cylinder) and is calcined. Due to the tilting and slow rotation of the cylinder, the material both rolls in a circular direction and moves axially (from the high end to the low end) to produce clinker that is cooled by the kiln head hood into the cooler. The fuel is sprayed into the kiln from the kiln head and the exhaust gases from the combustion are exchanged with the material and then exported from the kiln tail.
Metallurgical rotary kiln Features And Advantages
The new metallurgical rotary kiln has a simple structure, convenient and reliable control of the production process, few wearing parts, high operation rate and high quality of the kiln output.
1、The kiln body is made of calming carbon steel or alloy steel plate rolled and automatically welded.
2、The wheel belt, carrier wheel and open gear are made of alloy cast steel.
3、The sliding bearing adopts large clearance non-scraping tile bearing.
4、The transmission device adopts hardened gear reducer, elastic diaphragm coupling, DC motor dragging.
5、Adopting hydraulic stop wheel.
6、The head and tail of the kiln are sealed by scale stacking and cylinder pressing respectively.
7、With slow speed drive device.
Metallurgical rotary kiln Technical Parameter
Specification
(m) | Kiln Size | Power
(kw) | Wight
(t) | Remarks |
| Diameter(m) | Length(m) | Slope(%) | Capacity
(t/d) | Speed
(r/min) |
| Φ2.5×40 | 2.5 | 40 | 3.5 | 180 | 0.44-2.44 | 55 | 149.61 |
|
| Φ2.5×50 | 2.5 | 50 | 3 | 200 | 0.62-1.86 | 55 | 187.37 |
|
| Φ2.5×54 | 2.5 | 54 | 3.5 | 280 | 0.48-1.45 | 55 | 196.29 | Kiln decomposition kilns |
| Φ2.7×42 | 2.7 | 42 | 3.5 | 320 | 0.10-1.52 | 55 | 198.5 | ------ |
| Φ2.8×44 | 2.8 | 44 | 3.5 | 450 | 0.437-2.18 | 55 | 201.58 | Kiln decomposition kilns |
| Φ3.0×45 | 3 | 45 | 3.5 | 500 | 0.5-2.47 | 75 | 201.94 | ------ |
| Φ3.0×48 | 3 | 48 | 3.5 | 700 | 0.6-3.48 | 100 | 237 | Kiln decomposition kilns |
| Φ3.0×60 | 3 | 60 | 4 | 800 | 0.3-2 | 100 | 310 | ------ |
| Φ3.2×50 | 3.5 | 50 | 4 | 1000 | 0.6-3 | 125 | 278 | Kiln decomposition kilns |
| Φ3.3×52 | 3.3 | 52 | 3.5 | 1300 | 0.266-2.66 | 125 | 283 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ3.5×54 | 3.5 | 54 | 3.5 | 1500 | 0.55-3.4 | 220 | 363 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ3.6×70 | 3.6 | 70 | 3.5 | 1800 | 0.25-1.25 | 125 | 419 | Waste heat power kilns |
| Φ4.0×56 | 4 | 56 | 4 | 2300 | 0.41-4.07 | 315 | 456 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.0×60 | 4 | 60 | 3.5 | 2500 | 0.396-3.96 | 315 | 510 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.2×60 | 4.2 | 60 | 4 | 2750 | 0.41-4.07 | 375 | 633 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.3×60 | 4.3 | 60 | 3.5 | 3200 | 0.396-3.96 | 375 | 583 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.5×66 | 4.5 | 66 | 3.5 | 4000 | 0.41-4.1 | 560 | 710.4 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.7×74 | 4.7 | 74 | 4 | 4500 | 0.35-4 | 630 | 849 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ4.8×74 | 4.8 | 74 | 4 | 5000 | 0.396-3.96 | 630 | 899 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ5.0×74 | 5 | 74 | 4 | 6000 | 0.35-4 | 710 | 944 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ5.6×87 | 5.6 | 87 | 4 | 8000 | Max4.23 | 800 | 1265 | Preheating decomposition kilns |
| Φ6.0×95 | 6 | 95 | 4 | 10000 | Max5 | 950×2 | 1659 | Preheating decomposition kilns |